Key Takeaways
- Generators convert fuel into electricity and are ideal for high-capacity, long-duration backup power in industrial, commercial, or large-scale applications, offering flexibility with options such as silent, 3 phase, and portable models.
- Inverters use stored battery or solar energy to provide quiet, clean backup for essential appliances in residential or small office settings, limited by battery capacity and load size.
- Generators offer extended runtime and are suitable for powering entire facilities, but require regular maintenance, fuel supply, and may produce noise unless using silent models.
- Inverters excel in noise-sensitive environments, require minimal maintenance, and deliver stable power for sensitive electronics, but may not support heavy machinery or long outages.
- Choosing between an inverter and a generator depends on factors such as load size, required runtime, noise tolerance, budget, and the specific operational environment.
- Regular generator services and expert advice can maximise reliability, lifespan, and efficiency, ensuring you select the most suitable power solution for your needs.
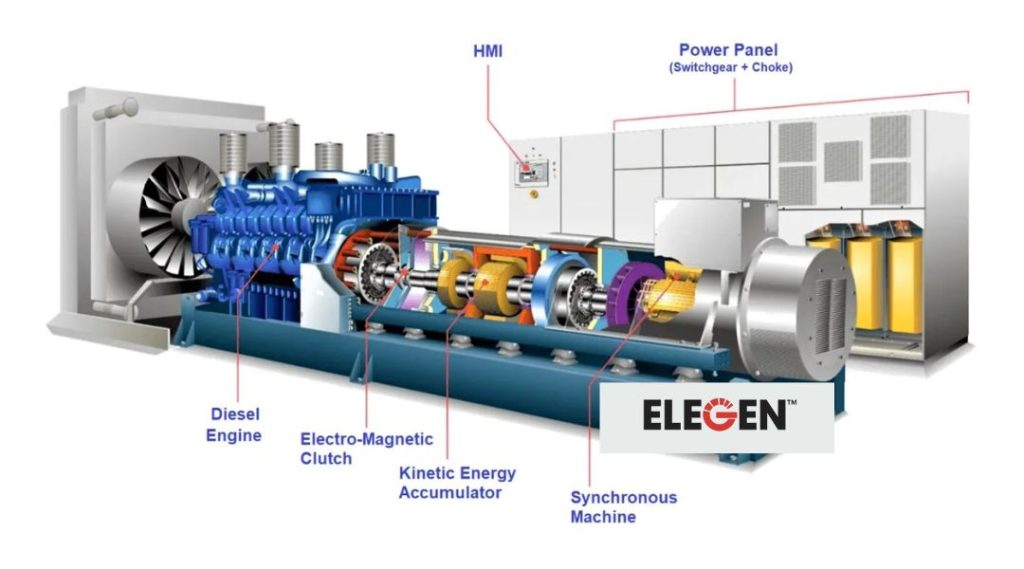
Overview Of Power Solutions
Different power solutions enable homes, businesses, and industries in South Africa to keep operations running when the grid falters. We see a broad spectrum here, from inverter units suited for essential appliances, to robust diesel generators supporting manufacturing plants and multi-storey buildings. Understanding their differences gives us a clear way to match technology to actual site needs.
Generators in Modern Power Backup
Generators transform fuel energy—most commonly diesel—into reliable electrical power. Models include silent generators for noise-sensitive environments, silent diesel generators for operations like food production, and 3 phase diesel generators, essential for heavy machinery and large commercial premises. For example, a 3 phase diesel generator supplies stable, high-capacity power for industrial welding or refrigeration units. Our Cummins generator and Stamford-OEM solutions maintain industry standards for uptime, crucial in sensitive environments like medical labs or data centres.
Generator hire options bring flexibility for seasonal businesses and construction sites where purchasing a unit outright isn’t practical. On top of that, generator services—such as regular inspections, voltage regulation upgrades, and part replacements—keep systems running at their best.
Inverters for Smaller Loads
Inverters cover the gap for users who want to power essential appliances—lights, laptops, and routers—in living spaces or smaller offices. They store power in batteries and later convert it for use during outages. Because inverters don’t operate with moving parts or combustion engines, they offer silent operation, unlike traditional diesel generators. However, the total runtime and wattage are limited by battery capacity. Inverter setups suit backup power for up to several hours, provided the connected load stays within system limits.
Choosing the Right Solution
Picking between inverters and generators depends on usage, budget, noise tolerance, and fuel supply. For uninterrupted manufacturing, a diesel generator provides the needed muscle. In contrast, for residential peace of mind during brief grid interruptions, an inverter offers low-maintenance peace and silence.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Generator (Diesel/Silent) | Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Suitable Applications | Industrial, commercial, backup | Domestic, small office |
| Power Range | 10 kVA – 2000+ kVA | 0.5 kVA – 10 kVA |
| Runtime | Unlimited (with fuel) | Limited (battery size) |
| Noise Level | Moderate – Low (silent models) | Silent |
| Maintenance | Regular servicing needed | Minimal |
| Example Brands | Cummins, Stamford, Volvo | Various brands |
| Fuel Needed | Diesel, petrol, gas | No direct fuel |
For further details, our team at ELEGEN can offer expert advice drawn from years of generator design, servicing, and solutions in African and global environments. Reliable power solutions let us focus on core business, not power interruptions.
What Is A Generator?
A generator’s main job is turning fuel into usable electrical power. We use generators all over Africa for backup power, industrial operations and sites where dependable energy is essential. Our team at ELEGEN offers expert advice and a full range of generator services, from consultation and design to generator hire, manufacturing and repair services.
Types Of Generators
Generators come in several types to meet diverse needs:
- Silent generator: These units operate with acoustic enclosures, making them suitable for hospitals, offices or any environment where noise levels need managing.
- Diesel generators: Favoured for their durability and efficiency, diesel generators are a strong choice for factories, data centres, and remote sites.
- 3 phase diesel generator: Designed for heavy industrial usage, 3 phase diesel generators deliver reliable power for large equipment—think mines, manufacturing and large-scale facilities.
- Portable generators: Smaller, mobile units work well on construction sites or for event support where temporary power is required.
- Fixed/standby generators: Installed permanently, these generators automatically provide backup electricity during outages, keeping operations stable.
For those needing temporary solutions, we provide generator hire options tailored to commercial and industrial projects.
How Generators Work
Generators create electricity by converting mechanical energy from fuels such as diesel, petrol or gas into electrical power. The basic process uses an engine (like a Cummins generator engine or Perkins), an alternator (often Stamford or Marelli), and a control system. Here’s a quick overview:
- Fuel supply: Diesel or petrol fuels the engine.
- Engine operation: The engine spins a shaft using the mechanical energy from fuel combustion.
- Alternator function: The spinning shaft turns the alternator’s rotor, generating alternating current (AC) electricity by electromagnetic induction.
- Voltage regulation: Control systems maintain steady output and protect connected equipment.
- Exhaust and cooling: These systems extend generator life and ensure safe use, especially in silent diesel generator options.
We partner with leading brands, like Cummins, Perkins, Volvo, Stamford, Marelli, Mecc Alte, for generator manufacturing, ensuring reliable power and full aftersales support. Regular generator repair services and scheduled maintenance help prevent breakdowns and maximise lifespan.
Generators keep production lines moving, servers online and critical infrastructure safe during outages. That’s why, whether you’re seeking generator services or advice on choosing the right model, our ELEGEN team’s always ready to help with expert guidance backed by industry leadership across Africa.
What Is An Inverter?
An inverter is a device that changes direct current (DC) from batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) for running standard appliances and equipment. Inverters provide backup power for homes, offices, and small businesses where quiet operation and low maintenance are important. They deliver electricity instantly during outages, which benefits environments using sensitive electronic devices or low-consumption appliances.
Types Of Inverters
Different types of inverters deliver power based on the requirements of the connected load, making it essential to select the right model for each use case.
- Pure sine wave inverters supply clean, stable AC power that matches grid quality, suitable for sensitive devices like computers and medical equipment.
- Modified sine wave inverters generate a more basic output that works for durable items such as tools and simple appliances, though they’re less suitable for sensitive electronics.
- Grid-tied inverters connect to the main power supply, supporting self-consumption and exporting surplus power to the grid, mostly used with solar systems.
How Inverters Work
Inverters power devices by converting stored DC energy, typically found in batteries or solar sources, into AC power. The inverter senses a loss of grid power then immediately draws energy from its batteries. Internal electronic circuits rapidly adjust voltage and current to fit the needs of home or office equipment, ensuring a seamless supply until the batteries are depleted or grid power returns. Unlike diesel generators or silent generators, inverters run silently and require little intervention, making them reliable for those who prioritise noise reduction, energy efficiency, and lower running costs.
What’s The Difference Between An Inverter And A Generator?
Knowing the difference between an inverter and a generator keeps essential systems running during outages. Each power solution comes with unique functionality best suited to specific needs, capacities, and environments.
Key Technical Differences
Generators deliver electrical power by converting chemical energy from fuels like diesel into mechanical energy, and then into electricity through an alternator. For example, silent generators and silent diesel generators use advanced insulation and sound-proofing to reduce operational noise, making them ideal for noise-sensitive areas.
Inverters convert direct current (DC) stored in batteries or produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for appliances. The pure sine wave output from a quality inverter ensures compatibility with sensitive devices, whereas generators provide raw AC power, suitable for high-demand equipment and industrial tools.
Generators operate independently from any battery storage, with run time only limited by fuel supply. Inverters, however, depend on the capacity of the battery bank for runtime—once depleted, output stops unless the batteries recharge.
Power output capacity marks a clear distinction. 3 phase diesel generators, for instance, handle heavy industrial loads with stable voltage across multiple phases, while inverters mainly support small- to medium-sized equipment in residential or small commercial setups.
Applications And Use Cases
Generators remain the backbone for large-scale or critical power applications. In sectors like food production or commercial manufacturing, diesel generators, such as Cummins generators, offer reliable backup to prevent downtime. Silent diesel generators serve hospitals or offices where noise reduction is critical, and generator hire options allow seasonal or short-term flexibility for construction projects or events.
Corporates reach for 3 phase diesel generators or robust fixed units when stability and capacity are necessary. Generator repair services and routine generator services, such as voltage regulation or control panel upgrades, lengthen the operational lifespan and reduce unexpected failures, notably important in continuous production settings.
Inverters, on the other hand, excel in domestic environments, small businesses, or off-grid solutions where minimal sound and low emissions matter. An inverter system powers computers, lighting, and Internet routers during outages without the smell or noise of combustion.
Choosing between an inverter and a generator depends most on power requirements, noise tolerance, available fuel sources, and whether backup is needed for essential or full-facility loads. For reliable, scalable solutions, we supply both silent generators and customised diesel generator systems, including service and support for ongoing peace of mind.
Pros And Cons Of Inverters And Generators
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of inverters and generators simplifies the process when selecting backup power. Both options deliver unique benefits, but their fundamental differences influence everything from usage to ongoing generator services and support.
Advantages Of Inverters
- Quiet Operation
Inverters run silently, making them ideal for residential or office environments where noise can disrupt daily activities.
- Clean Power Output
Pure sine wave inverters produce stable power, protecting sensitive electronics such as computers, medical devices, and communication equipment.
- Low Maintenance
Inverters require minimal upkeep compared to engines in diesel generators, reducing long-term maintenance needs.
- Energy Efficiency
Inverters convert stored energy from batteries with high efficiency, especially when supplying small or medium loads.
- Compact And Portable
Most inverter systems are smaller and lighter, making installation easier and offering greater placement flexibility indoors.
Advantages Of Generators
- High Power Capacity
Generators, including silent generators and 3 phase diesel generators, handle substantial loads for commercial and industrial settings. These solutions keep factories running and support large engineering environments.
- Extended Runtime
Generators supply power as long as fuel (diesel or petrol) is available, ideal for long outages or off-grid use.
Diesel generators are common for backup power in manufacturing, food production, and general commercial spaces.
- Versatility In Application
Units such as cummins generators and silent diesel generators adapt to wide-ranging needs, from fixed standby to portable and rental systems via generator hire.
- Independence From Battery Storage
Generator power output isn’t limited by battery storage. Operation continues without risk of sudden shutdown from depleted batteries.
- Comprehensive Support And Parts
Ongoing generator services, like generator repair services, cover scheduled maintenance, control panel upgrades, and voltage regulation adaptations for reliability.
Limitations Of Both Technologies
- Fuel Dependence And Noise (Generators)
Generators need a constant supply of fuel, which incurs operating costs and logistics. Non-silent units produce noise and emissions, which can be unsuitable in urban or noise-sensitive environments.
- Battery Dependency And Runtime (Inverters)
Inverter runtime depends entirely on battery capacity. Larger battery banks increase cost and space requirements, and frequent power cuts could outlast the stored energy.
- Load Limitations
Inverters support only essential or designated loads. Most inverters can’t run heavy machinery or large heating elements, making generators necessary for high-consumption applications.
- Setup And Space
Generators, especially diesel units or those used for generator hire, require ample space, correct ventilation, and compliance with safety regulations—a factor less relevant to most compact inverters.
Weighing these pros and cons clarifies which power solution best aligns with site needs, operational scale, and long-term support expectations—key factors for businesses that rely on stable, expert-backed generator services.
Which One Should You Choose?
Selecting between an inverter and a generator depends on the exact needs of your power backup situation, the scale of your facility, and your operational priorities.
- Load Size and Power Needs
Inverters provide backup for small to medium loads, ideal for homes and offices supporting devices like laptops, lights, or routers. Generators supply power for larger or whole-facility operations, running heavy machinery, air conditioning, and production lines. Environments such as food production, manufacturing, and sensitive commercial facilities rely on diesel generators or 3 phase diesel generators for consistent and high-capacity output.
- Duration and Runtime
Generators, including silent generator or silent diesel generator models, run for long periods as long as fuel is available, making them suitable for businesses needing uninterrupted operation in off-grid or load shedding scenarios. Inverters operate only as long as batteries last, which restricts their effectiveness for extended outages or full-site coverage.
- Noise and Environmental Sensitivity
Inverters remain nearly silent, which fits offices, clinics, and noise-sensitive businesses. Silent generator options, however, minimise operational noise, making them appropriate for sites where lower decibel output is required by regulation or comfort.
- Maintenance and Service
Inverters require little ongoing attention aside from battery checks. Generator services become critical for business continuity, with generator repair services maintaining performance over time. Companies like ours also offer generator hire, ensuring rapid scalability or short-term rental for events and seasonal needs.
- Fuel and Running Costs
Diesel generators offer robust and cost-effective power, depending on diesel supply. Inverters draw from batteries, often linked to solar or grid charging — they lack running costs during operation, except for eventual battery replacement.
- Application Environment
Large manufacturing, engineering works, big retail, or sensitive industries often implement generators due to higher reliability and load range. Homes, small shops, and offices typically go for inverters for uninterrupted, low-noise backup with limited loads.
By aligning the technology — whether a generator or inverter — with demand, environment, and site-specific challenges, users gain resilience and cost-efficiency. Choices such as generator hire and silent diesel generator deployments support dynamic requirements. For extended scalability, 3 phase diesel generator units and custom generator services handle industrial complexities, while a simple inverter offers immediate, silent relief for small operations or residential needs.
Conclusion
Selecting between an inverter and a generator means matching your specific power needs and operational context with the right technology. Generators, especially diesel generators, support higher loads, uninterrupted runtime and broad application across industrial, commercial or sensitive environments. Silent generators, including those fitted with noise-reducing technology, offer solutions where a quiet work environment comes first. When downtime isn’t an option, generator hire provides immediate access to backup power, whether the need lasts days or months.
Generator services extend far beyond installation. Regular generator repair services and maintenance checks help maintain reliability, boost lifespan and prevent sudden breakdowns in critical operations. Our authorised partnerships, such as with Cummins, enable us to provide 3 phase diesel generator solutions for robust industrial applications, and advanced OEM engine support for specific performance criteria.
For homes or offices, inverters present benefits including silent operation, energy efficiency and low maintenance, with limitations largely defined by battery size and load. In cases where seamless, silent backup is most important, inverters might prove more appropriate than generators.
Evaluating key parameters—total load, desired runtime, noise tolerance, maintenance planning and operational environment—results in a sound investment. Generator repair services and full-scope generator services ensure ongoing security and efficiency for every use case. Our tailored approach, informed by years of experience and deep technical partnerships, guides you toward the right solution—be it silent diesel generators for sensitive applications or generator hire for temporary projects.
Elegen | Generator Manufacturer South Africa
Address: 23/24 Mountjoy St, Wilbart, Edenvale, 1609
Phone: 011 455 4900
Google Maps: Find us here
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between an inverter and a generator?
An inverter converts DC power from batteries or solar panels into AC power for appliances, while a generator produces electricity by converting mechanical energy from fuels like diesel or petrol. Inverters are quieter and low-maintenance, but their use is limited by battery capacity, whereas generators can supply larger loads for extended periods, limited mainly by their fuel supply.
Which is better for home use: an inverter or a generator?
For most homes, inverters are better for essential appliances due to their silent operation, energy efficiency, and low maintenance. However, if you need to run heavy-duty equipment or multiple large appliances for long periods, a generator may be more suitable.
Can I use an inverter for my business during load shedding?
Yes, inverters are ideal for small offices and businesses where silent operation is important. They work well with essential equipment but might not support high-power machinery or extensive setups. For larger business needs, a generator is usually the better option.
How do silent generators differ from standard generators?
Silent generators feature soundproof enclosures or advanced muffling technologies to reduce noise during operation. They are designed for environments where noise reduction is critical, such as hospitals, schools, or residential areas.
Are generators more reliable than inverters during long power outages?
Generators are generally more reliable for extended outages because they can run continuously as long as there is enough fuel. Inverters depend on the size of their battery bank, so their runtime is limited unless the batteries are regularly recharged.
What maintenance do generators and inverters require?
Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, filter replacements, and routine inspections. Inverters need less maintenance, mostly involving battery checks and ensuring good ventilation. Both systems benefit from periodic checks to maintain performance and longevity.
Is generator hire a good solution for seasonal or temporary needs?
Yes, generator hire is an excellent option for businesses or events with temporary or seasonal power needs. It allows for immediate backup power without the upfront costs of purchasing a generator and includes professional installation and maintenance services.
Can inverters power heavy machinery?
No, most inverters are designed for light or moderate loads like home appliances, computers, and lights. Heavy-duty machinery typically requires a generator due to the high power demand and longer runtime.
What type of generator is best for industrial use?
Diesel generators, particularly three-phase models, are preferred for industrial use as they offer durability, high power output, and efficiency when running heavy-duty equipment and supporting large facilities.
How do I choose between an inverter and a generator?
Consider your power requirements, the type of equipment you need to run, desired noise levels, available budget, and how long you need backup power. Inverters are ideal for essential, low-power loads and quiet operation, while generators are better for heavy, continuous loads and longer outage periods.
